On the risk of money laundering in credit card business
In the traditional concept, credit cards are often used by cashing, and after paying a certain handling fee, the credit line that is limited to consumption is illegally discounted through POS machines. In recent years, public security organs, banks and other parties throughout the country have launched a "card-breaking" campaign to severely crack down on illegal activities such as selling telephone cards and bank cards. In this context, many banks have increased the transaction restrictions on debit card accounts. Criminals began to turn money laundering carriers to credit card accounts with relatively loose control. Credit card crimes are increasingly characterized by gangs and cross-regions, and various crimes such as fraud and gambling frequently transfer stolen money. Based on practical work and internal and external cases, this paper discusses the money laundering of credit card business from the recent common means of money laundering.
I. Similarities and differences in debit and credit card business
In a narrow sense, a credit card refers to a credit card, which is an electronic payment card issued by a bank and gives the cardholder a certain credit limit, within which the cardholder can spend first and then repay. The customer base of credit card is generally a group with certain consumption and repayment ability, but in recent years, the customer base of credit card has been sinking, and the overall customer base has been converging to debit card except that the credit limit of different customers may be different. Credit cards are mainly used for consumption and cash withdrawal, and also have the deposit and transfer functions of debit cards. Generally speaking, credit cards have most functions of debit cards.
On November 13, 2015, the China Banking Regulatory Commission issued the Notice on the Work Matters Related to the Banking Industry’s Combating and Governing New Crimes in Telecommunication Networks. Since January 1, 2016, the same customer may not open more than four debit cards in the same institution in principle (excluding social security cards). From 2015 to 2016, the People’s Bank of China successively issued the Notice on Improving Personal Bank Account Services and Strengthening Account Management, the Notice on Strengthening Payment and Settlement Management and Preventing New Crimes in Telecommunication Networks, and the Notice on Implementing the Classified Management System of Personal Bank Accounts, established the classified management of debit card accounts, and strengthened the handling and use restrictions on Class I, II and III debit card accounts. Credit card account management is independent of debit card, and its management is not covered in the above regulatory documents. The most important thing about credit card management is always the regulation in the Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Credit Card Business of Commercial Banks, which has been used since 2011, mainly for the relevant requirements that entity credit cards must be pro-nuclear and pro-visit.
Second, the common means of money laundering by credit cards
(A) the use of overpayments to launder money
Overpayment, also known as overflow deposit, refers to the extra money paid by credit card customers when they deposit or the money deposited in credit card accounts. Money deposited in the credit card center will not increase any interest. Then why do customers put money into their credit cards? One is to transfer to wrong account. I wanted to transfer money to a debit card, but I mistakenly transferred it to a credit card. If the amount of the transfer is large, customers will generally withdraw cash from the credit card or transfer money from the credit card to the debit card, and usually use free channels; One is to prevent yourself from missing your credit card, and customers usually save money on the billing date or around the deposit date; Another is to use overpayment to commit money laundering crimes.
There is no limit to cash withdrawal and transfer at the counter of overpayment, and other channels generally have only daily limit. Overpayment can simultaneously increase the consumption limit of the account. In addition, with the increasingly fierce market competition and the constant guidance and encouragement from the regulatory authorities to the banking industry to "reduce fees and make profits", most credit card overpayment cash withdrawal and transfer policies are implemented, and domestic banks in the same city are exempt from handling fees, and self-service banks in the same city are charged symbolically, and the proportion of charging items in other channels is also controlled within one thousandth and the highest fees are set.
By using overpayment and paying lower costs, the excessive (large) funds can be dispersed and quickly realized, which also makes it one of the most common means of credit card money laundering in the near future. Criminals set up a multi-layer fund cleaning account system by nesting credit card accounts, taking advantage of the information asymmetry between banks, banking institutions and payment institutions, and quickly transferring funds through channels such as fast payment. Furthermore, criminals trick victims into depositing or directly transferring the defrauded money and gambling money into credit card accounts held by money laundering gangs, and then cut off the transaction link or obscure the transaction source by withdrawing cash, transferring money, forging POS or online shop transactions.
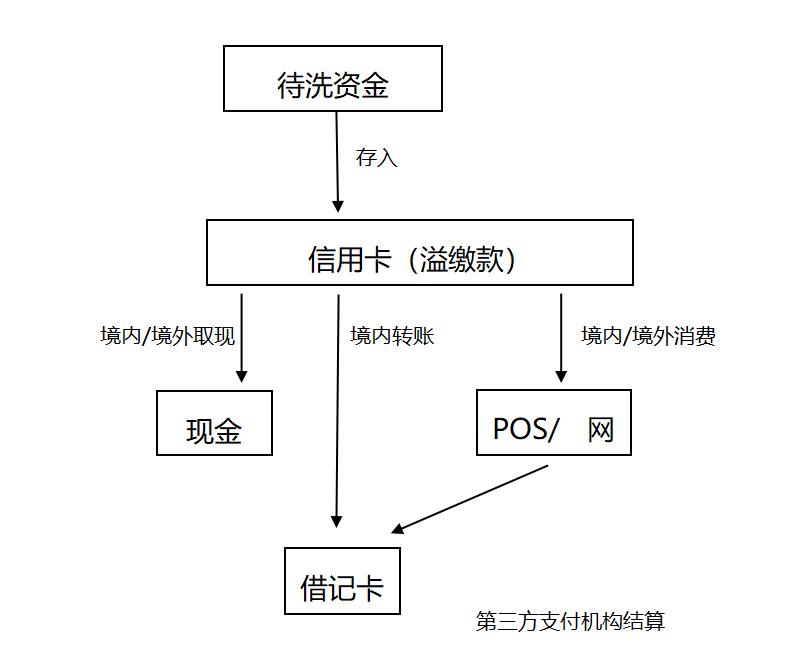
Figure 1. Main patterns of money laundering by overpayment
Using overpayment to launder money, transactions often show the characteristics of decentralized transfer to centralized transfer; The funds are fast-forward and fast-out, and the funds are transferred out by transfer or consumption on the same day after being transferred in multiple amounts, and the transitional nature of the account is obvious; The trading time is abnormal, and there may be a lot of early morning trading. The frequency of deposit is high, and the number of deposits per month is ten or one hundred; There are many opponents in the deposit, and many banks across the country are involved in inter-bank transfer; Most of the single deposit amount is an integer multiple or has a special mantissa, which does not rule out the suspicion of splitting; There are high-frequency large-scale cash withdrawals from different places or overseas, and you don’t mind the handling fee. The monthly consumption of customers is high, usually more than one million, which is inconsistent with their identity; The monthly consumption is as high as 10 times or 100 times of the original credit line; Counterparties are mainly special merchants or third-party payment institutions, which are relatively concentrated; At the end of the adjustment, customers usually say that they have transferred their credit cards by mistake or are familiar with the use rules of credit card overpayment transfer and cash withdrawal.
(2) using supplementary cards to launder money
The supplementary card is relative to the main card. Each cardholder who opens a credit card can apply for a supplementary card for other natural persons with full capacity for civil conduct, or natural persons with limited capacity for civil conduct who are over 11 years of age (different banks have different regulations). The supplementary card can share the line with the main card, and the cardholder of the main card and the cardholder of the supplementary card bear joint and several liabilities for the debts. Supplementary card holders must be immediate family members of the main credit card applicant, including parents, spouses, children, etc.
In most banks, the affiliated cardholders do not belong to customers, but as potential customers, the application for the affiliated cardholders only needs to be initiated by the main cardholder and the ID card of the affiliated cardholders can be provided. Although the bank requires that the affiliated cardholders can only apply for relatives, it is difficult to verify the relationship materials, which often becomes an option for customers to fill in actively. In addition, compared with the rigid retention of the 9 elements of the identity information of the main card, there are too many comprehensive requirements for the retention elements of the identity information of the auxiliary card holder.
Supplementary cards can be applied for and used by customers who do not meet the requirements for handling the main card. Because of the low level of face-to-face signing, there is still the risk of providing services for impersonation and anonymous objects. Criminals can collect other people’s supplementary cards in batches, bind the supplementary cards through off-counter channels to open multiple Class II debit card accounts, and then use Class II accounts to deposit money from unbound accounts to collect upstream gambling or fraudulent funds, and then transfer money to other debit card accounts quickly. In addition, in cross-border money laundering, by taking advantage of the characteristics that supplementary cards share the credit limit of the main card, we can support large-scale overseas consumption by continuously overpaying funds to the main card, thus breaking through the exchange restrictions and forming a special "underground money house" money laundering model.
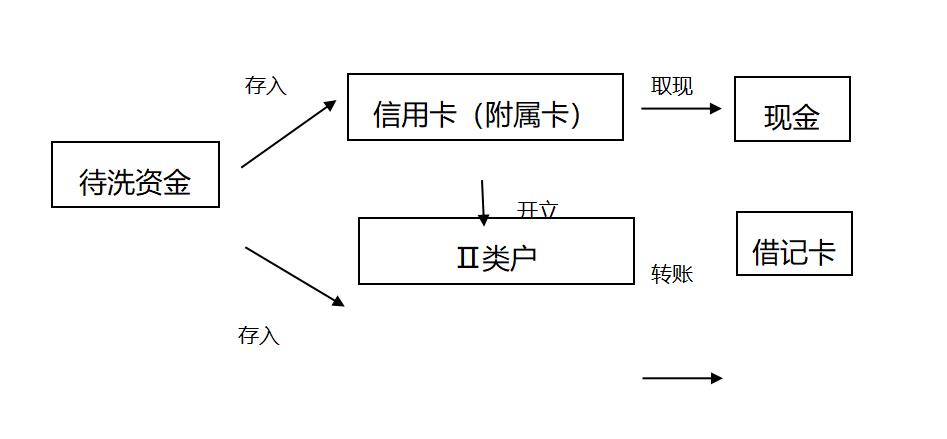
Figure 2. Main patterns of money laundering by supplementary cards
Using supplementary cards to launder money, the main cardholder often applies for multiple supplementary cards for multiple people repeatedly; A large number of main cards applying for supplementary cards have cross-correlation relations; The authenticity of the documents provided when applying for supplementary cards is in doubt, and the act of repeatedly applying for supplementary cards by using forged documents and filling in false relationships; The relationship between the main cardholder and the supplementary cardholder is abnormal, just as a main cardholder applies for supplementary cards for more than 5 people, but the relationship is filled in by spouses, parents or children; The age of the supplementary cardholder does not match the relationship between the main supplementary cardholder; Multiple supplementary cards have been applied for the same mobile phone number; Principal cardholders apply for supplementary cards with each other; Frequent users of the same supplementary card; Transactions in supplementary cards are not frequent, many cards have no transaction records or transactions are scattered to all cards under their names.
Similar to the supplementary card, there is also a mobile phone credit card (virtual card), which is a credit card that banks apply for and activate by video in the network of first-tier cities, and its application scope is the same as that of credit cards. You can apply separately, or you can apply together with the physical card, which can meet the customer’s immediate use of the card. Virtual card and physical card are the same card product sharing quota, which can be used separately and do not affect each other. Traditional credit cards need to be able to apply online, but they need to be signed offline, while virtual credit cards can apply online and sign online at the same time. Simplify the card issuing process and optimize the customer experience, at the same time, simplify the process of full adjustment and weaken the requirements of full adjustment, which not only increases the pressure on customer identification, but also makes it easier to become a springboard to hide the source and destination of funds.
Third, credit card money laundering risk control recommendations
(1) Improve the monitoring rules for credit card transactions. Judge the unique suspicious characteristics of credit cards such as overpayment and supplementary cards, and establish a multi-dimensional monitoring model based on transaction time, amount, location and frequency. Such as limiting the number of expenses, the number of cards, application channels, etc. Pay attention to the overpayment of customers’ monthly bills, at the same time, increase the monitoring of overpayment amount after a single transaction, improve the dynamic characterization ability of overpayment amount, and improve the accuracy of monitoring and analysis of customers’ transaction behavior; Accurately and comprehensively incorporating supplementary card transactions into transaction monitoring can not only match the model of supplementary card transactions alone, but also comprehensively analyze the transactions of principal cardholders, paying attention to the characteristics of gangs.
(2) Strengthen due diligence requirements. Implement the identity verification mechanism of cardholders and users, such as face recognition, online verification, list screening, mobile phone real-name registration system verification, image comparison and other cross-verification, and appropriately request supplementary certification materials and elements collection scope for high-risk customers. Timely discover customers’ large overpayment behavior, verify the reasons for the overpayment with customers, pay attention to the source of funds, comprehensively analyze customers, transactions and behaviors with obvious anomalies, and conduct money laundering risk investigation in time. For those who cannot rule out the suspicion of money laundering, report the suspicion in time and implement the control of different accounts of the same customer.
(3) Implementing effective credit card control measures. Strengthen the management of overpayment, repayment by others and abnormal card use behavior, take management measures such as warning, restricting repayment transactions, lowering credit line and stopping payment for cardholders suspected of abnormal behavior, and dynamically adjust the control measures. In order to meet the reasonable deposit demand of cardholders, the cumulative limit of billing cycle and the limit of the number of transactions per day will be increased for deposits or overpayments from non-bank debit cards or non-bank channels to our credit cards. Adjust the transaction limit of the cardholder’s credit card overpayment under the condition of meeting the cardholder’s reasonable consumption demand.
(4) Do a good job in data governance and system construction. Continue to carry out data governance to ensure that customer information of credit cards and related business systems can be shared and updated in real time. Fully consider the needs of anti-money laundering work, break down system barriers, bring all transactions of credit card business into the monitoring scope of anti-money laundering system, collect customer information and transaction elements completely, accurately and comprehensively, continuously strengthen the comprehensive analysis ability of debit and credit cards, and improve the efficiency of abnormal transaction screening personnel. Use blockchain technology to clear the context of funds and prevent possible risk loopholes.
(5) Strengthen publicity and education for customers. Remind customers to keep personal information properly. Credit cards are only for their daily consumption, and they are not allowed to rent, lend or sell personal credit cards or give them to others in other ways. Do not use the credit card to accept funds from unknown sources in other people’s names, or transfer funds from unknown sources in my credit card through false applications and transactions, and do not use it for illegal transactions such as telecommunication network fraud, online gambling, underground money houses, etc.